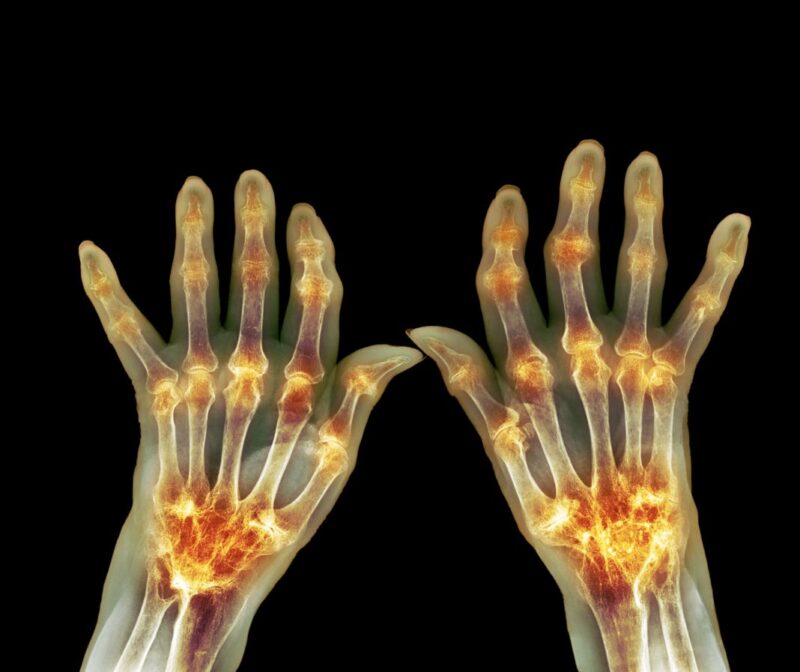
(Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News) — Scientists report specific dissimilarities in mouth microbial compositions among patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (ERA) and those at risk of developing the disease, compared with healthy individuals who were not at risk.
The findings come from a study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology titled, “The oral microbiome in early rheumatoid arthritis patients and individuals at risk differs from healthy controls.”
“Prevotella and Veillonella—both gram-negative anaerobes—were at higher relative abundance in saliva, and Veillonella was also at higher relative abundance in tongue coating, of both early rheumatoid arthritis patients and at-risk individuals compared to healthy controls,” the authors note. (…)