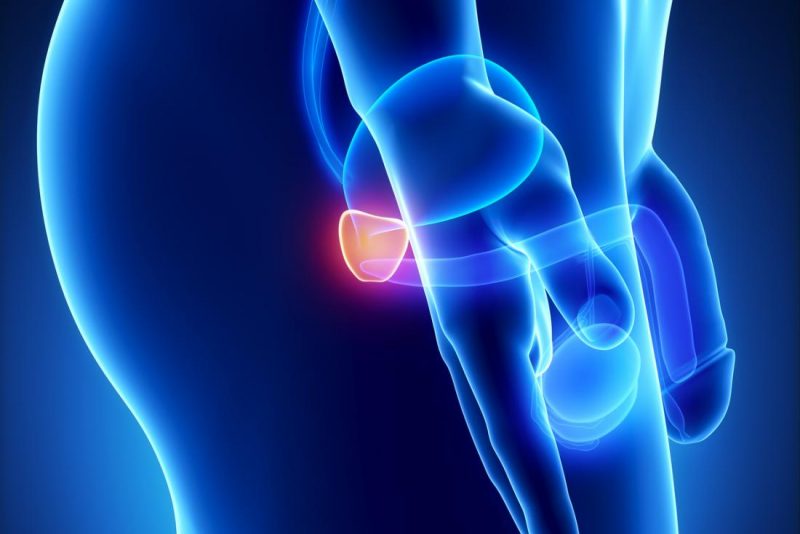
(Christian Nordqvist/ MedicalNewsToday) — Prostate cancer affects the prostate gland, the gland that produces some of the fluid in semen and plays a role in urine control in men.
The prostate gland is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum.
In the United States (U.S.), it is the most common cancer in men, but it is also treatable if found in the early stages.
In 2017, the American Cancer Society predicts that there will be around 161,360 new diagnoses of prostate cancer, and that around 26,730 fatalities will occur because of it.
Regular testing is crucial as the cancer needs to be diagnosed before metastasis.
What is prostate cancer?
The prostate is a walnut-sized exocrine gland. This means that its fluids and secretions are intended for use outside of the body.
The prostate produces the fluid that nourishes and transports sperm on their journey to fuse with a female ovum, or egg, and produce human life. The prostate contracts and forces these fluids out during orgasm.
The protein excreted by the prostate, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), helps semen retain its liquid state. An excess of this protein in the blood is one of the first signs of prostate cancer. (…)